Conceptos básicos de la afección
¿Qué es el lupus (lupus eritematoso sistémico)?
El lupus es una enfermedad autoinmunitaria. Esto significa que el sistema natural de defensa del organismo (sistema inmunitario) ataca tejidos saludables en vez de atacar solamente cosas como bacterias o virus. Esto causa inflamación.
Algunas personas con lupus solo tienen síntomas leves. Pero la enfermedad es de por vida y puede agravarse. El lupus puede causar problemas con la piel, los riñones, el corazón, los pulmones, los nervios o los glóbulos sanguíneos.
El lupus eritematoso sistémico es el tipo más común y más grave de lupus. Pero existen otros tipos de lupus. Incluyen el lupus discoide o cutáneo, el lupus sistémico inducido por fármacos y el lupus neonatal.
¿Cuál es la causa?
No se sabe exactamente cuál es la causa del lupus. Los expertos creen que algunas personas nacen con ciertas mutaciones genéticas que afectan su sistema inmunitario y que las hacen más propensas a tener lupus.
¿Cuáles son los síntomas?
Los síntomas del lupus son muy variados, y aparecen y desaparecen. Los síntomas comunes incluyen sentirse muy cansado y tener dolor o hinchazón en las articulaciones (artritis), fiebre y salpullido. Es posible que tenga llagas en la boca y se le caiga el cabello. Con el tiempo, algunas personas con lupus tienen problemas del corazón, los pulmones, los riñones, los glóbulos o el sistema nervioso.
¿Cómo se diagnostica?
No hay una prueba única para el lupus. Su médico comprobará si tiene lupus revisándolo, preguntándole sobre sus síntomas y antecedentes de salud y haciendo algunos análisis de sangre y de orina. Se fijará en ciertos criterios para ayudar al diagnóstico de lupus. Estos criterios incluyen el salpullido en forma de mariposa e hinchazón articular.
¿Cómo se trata el lupus?
El tratamiento para el lupus puede incluir antipalúdicos para tratar la fatiga, el dolor articular y los salpullidos cutáneos, crema con corticoesteroides para los salpullidos y antiinflamatorios no esteroideos para dolores articulares o musculares leves y fiebre. Pueden recetarse pastillas de corticoesteroides si otros medicamentos no controlan los síntomas.
¿Cómo puede manejarse?
Uno de los objetivos de controlar los síntomas entre leves y moderados del lupus es prevenir las crisis. Usted puede:
- Descansar lo suficiente. Algunas personas que tienen lupus necesitan dormir hasta 12 horas todas las noches.
- Evitar el sol. Use filtro solar y use ropa protectora cuando se encuentre al aire libre.
- Hacer ejercicio en forma regular para prevenir la fatiga y la rigidez articular.
- Regular su ritmo. No haga demasiadas actividades.
- Dejar de fumar.
- Prestar atención a sus síntomas. Si parecen estar empeorando, tome medidas para controlarlos. Por ejemplo, si su fatiga, dolor o salpullido empeoran, puede ser una señal de una crisis.
- Hablar con su médico acerca de cualquier vacuna que pueda necesitar.
Con un buen cuidado personal, la mayoría de las personas que tienen lupus pueden seguir haciendo sus actividades cotidianas normales.
Ayude a sus familiares y a sus amigos a entender sus límites y necesidades cuando sus síntomas se agravan. Forme un sistema de apoyo con sus familiares, amigos y profesionales de la salud.
Qué aumenta su riesgo
Las probabilidades de tener lupus son más altas en personas que:
- Son mujeres.
- Son de raza negra.
- Tienen entre 15 y 45 años.
- Tienen antecedentes familiares de lupus.
- Toman medicamentos que están asociados con el lupus sistémico inducido por fármacos.
Síntomas
Los síntomas del lupus son muy variados, y aparecen y desaparecen. Los períodos en que se agravan los síntomas se llaman recaídas o crisis. Los períodos en que los síntomas están bajo control se llaman remisiones.
Los síntomas comunes incluyen:
- Fatiga. El aumento de la fatiga es una señal típica de que una crisis de síntomas está por suceder.
- Dolor o hinchazón articular (artritis).
- Fiebre.
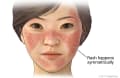
- Un salpullido cutáneo. Muchas personas tienen un salpullido en forma de mariposa en las mejillas y sobre el caballete nasal. Llagas en la piel o manchas rojizas que se descaman pueden aparecer en los brazos, las manos, la cara, el cuello o la espalda.
- La exposición a la luz ultravioleta (como la luz solar o camas solares) suele hacer que el salpullido empeore y puede desencadenar crisis de lupus.
- Llagas en la boca.
- Caída del cabello.
- Síndrome de Raynaud. Esto hace que los dedos de las manos y de los pies se vuelvan blancos y azules o enrojecidos. La piel se siente entumecida, fría y con hormigueo.
Con el tiempo, algunas personas con lupus tienen problemas del corazón, los pulmones, los riñones, la piel, los glóbulos sanguíneos o el sistema nervioso.
Qué ocurre
La evolución del lupus varía de persona a persona. Es difícil de predecir, porque los síntomas aparecen y desaparecen. Es posible que no note los síntomas por un tiempo prolongado. Pero, a veces, el lupus se presenta rápidamente.
Los períodos en que usted tiene síntomas se llaman crisis o recaídas. Las remisiones son los períodos en que sus síntomas están controlados. Las crisis y las remisiones pueden suceder abruptamente y sin una causa evidente. No hay manera de predecir lo seria que será una crisis ni cuánto tiempo durará. Durante una crisis, tal vez tenga nuevos síntomas además de los que ya tenía.
Los niños pueden tener lupus. Pero generalmente se presenta durante la adolescencia o más adelante. Cuando los órganos vitales están involucrados, el lupus en los niños se manifiesta de manera más grave que en los adultos.
También hay inquietudes si usted tiene lupus y está embarazada. Algunas personas con lupus tienen problemas renales y cardíacos. Pero la mayoría de las personas tienen una esperanza de vida normal o casi normal.
Cosas que provocan crisis de lupus
Ciertas cosas pueden provocar las crisis de lupus. Estas pueden incluir:
- Exposición a luz ultravioleta. Esto suele ser por la luz solar.
- Fumar. Fumar puede provocar crisis y también puede empeorarlas.
- Algunos medicamentos.
- Algunas infecciones. Algunas personas que tienen infecciones por citomegalovirus (CMV), parvovirus (como el eritema infeccioso) y hepatitis C en algún momento tendrán lupus. El virus Epstein-Barr se ha vinculado con el lupus en los niños.
- Exposición a sustancias químicas. Las toxinas químicas de las que se sospecha incluyen tricloroetileno en agua de pozos y polvo de sílice. Los tintes y alisadores de cabello, vinculados al lupus en el pasado, ya no se piensa que desencadenen lupus.
Sepa más
Cuándo llamar a un médico
Llame al 911 o a otros servicios de emergencia de inmediato si tiene síntomas de un ataque al corazón. Estos pueden incluir:
- Dolor, presión o una sensación extraña en el pecho.
- Sudoración.
- Falta de aire.
- Náuseas o vómito.
- Dolor, presión o una sensación extraña en la espalda, en el cuello, en la mandíbula, en la parte superior del abdomen, o en uno o ambos hombros o brazos.
- Aturdimiento o debilidad repentina.
- Latidos cardíacos rápidos o irregulares.
Después de llamar al 911, es posible que el operador le diga que mastique 1 aspirina de adulto o entre 2 y 4 aspirinas de dosis baja. Espere la ambulancia. No trate de conducir usted mismo.
Llame al 911 o a otros servicios de emergencia de inmediato si tiene alguna de las siguientes señales de ataque cerebral. Los síntomas de un ataque cerebral suceden rápidamente. Un ataque cerebral puede causar lo siguiente:
- Entumecimiento, hormigueo o debilidad o parálisis repentinos en la cara, el brazo o la pierna, sobre todo si ocurre en un solo lado del cuerpo.
- Cambios súbitos en la vista.
- Problemas repentinos para hablar.
- Confusión repentina o dificultad súbita para comprender frases sencillas.
- Problemas repentinos para caminar o mantener el equilibrio.
- Un dolor de cabeza intenso y repentino, distinto a los dolores de cabeza anteriores.
Llame a un médico ahora mismo si:
- Tiene falta de aire.
- Tiene sangre en la orina o está orinando con menos frecuencia y en cantidades menores de la habitual.
- Tiene fiebre con o sin dolor de cabeza y dolores corporales, pero no ha estado expuesto recientemente a un resfriado ni a la gripe.
- Tiene depresión o algún cambio de conducta o de pensamiento.
- Tiene entumecimiento u hormigueo en las manos o en los pies.
- Está mareado o tiene debilidad muscular.
- Tiene hinchazón en la parte baja de las piernas o en los pies.
Llame a un médico tan pronto como pueda si manifiesta algún síntoma nuevo de lupus. También llame a su médico si alguno de los síntomas que ha tenido por un período de tiempo empeora.
Si no se le ha diagnosticado lupus y tiene síntomas, como dolor articular, fatiga o salpullido en la piel, vea a su médico o dígale a su médico sobre sus inquietudes en la próxima visita con su médico.
A quién consultar
Para evaluar los síntomas iniciales y tratar el lupus leve, usted puede hablar con:
- Un médico de medicina familiar o un internista.
- Un reumatólogo.
- Un inmunólogo.
Para el manejo a largo plazo de un caso complicado de lupus, hable con:
- Un reumatólogo.
- Un inmunólogo.
Para casos más complicados de lupus, un reumatólogo suele ser el médico principal. Se consulta a otros especialistas cuando es necesario.
- Para problemas de salud mental, como depresión, ansiedad, psicosis u otros cambios de comportamiento, vea a su médico de familia o internista o a un psiquiatra.
- Para el tratamiento de problemas de órganos, un médico que se especialice en enfermedades de ese sistema de órganos en particular puede trabajar conjuntamente con un reumatólogo o inmunólogo. Los siguientes profesionales suelen tratar problemas de órganos vitales causados por el lupus:
Exámenes y pruebas
No hay una prueba única para el lupus. Dado que el lupus afecta a cada persona de diferente manera, puede ser difícil diagnosticarlo. Puede llevar tiempo para que se manifiesten los síntomas. Y, a veces, tarda de semanas a años en diagnosticarse.
Su médico le hará un examen y le hará preguntas acerca de sus síntomas y de sus antecedentes de salud. Se fijará en ciertos criterios para ayudar al diagnóstico de lupus. Estos incluyen un salpullido en forma de mariposa, hinchazón articular, fatiga, tener sensibilidad a la luz solar y llagas en la boca o la nariz.
Si tiene síntomas de lupus y tiene un resultado positivo de una prueba de anticuerpos antinucleares, es posible que no necesite pruebas adicionales.
Si su médico cree que necesita hacerse más pruebas, tal vez le hagan una o más de estas pruebas:
- Otras pruebas de anticuerpos en la sangre
- Estudio del complemento
- Velocidad de eritrosedimentación o proteína C reactiva
- Hemograma completo
- Análisis de orina
- Prueba del anticoagulante lúpico
Sepa más
Generalidades del tratamiento
El tratamiento del lupus puede ser complicado. Los síntomas varían, y las crisis y remisiones pueden seguir ocurriendo. Pero la meta del tratamiento es encontrar un equilibrio entre el control de los síntomas, la prevención de daño a los órganos y la reducción de efectos secundarios.
El tratamiento para el lupus leve puede incluir:
- Medicamentos antipalúdicos. Pueden tratar la fatiga, el dolor articular y muscular y los salpullidos en la piel.
- Crema con corticoesteroides para el salpullido.
- Medicamentos antiinflamatorios no esteroideos (AINE). Estos pueden tratar el dolor articular o muscular leve y la fiebre.
- Pastillas de corticoesteroides. Se usan si otros medicamentos no controlan sus síntomas.
Si su lupus causa o amenaza con causar daño a órganos, es potencialmente mortal o afecta seriamente su calidad de vida, es posible que también necesite tomar:
- Corticoesteroides en dosis más altas. Estos pueden ser en forma de pastillas o por vía intravenosa en el brazo (IV).
- Medicamentos que inhiban su sistema inmunitario (inmunodepresores).
Algunas personas tienen enfermedad renal grave que no puede controlarse con medicamentos. Podrían necesitar diálisis o un trasplante de riñón.
Sepa más
Cuidado personal
Reduzca el estrés y la fatiga
- Mantenga su programa diario tan simple como sea posible.
- Mantenga la lista de cosas pendientes tan corta como pueda.
- Haga ejercicio con regularidad. Caminar o nadar a diario, por ejemplo, puede reducir el estrés, despejarle la mente, mejorar su estado de ánimo y ayudarle a combatir la fatiga.
- Utilice meditación, yoga o imágenes guiadas para relajarse.
- Descanse lo suficiente. Algunas personas que tienen lupus necesitan dormir hasta 12 horas todas las noches.
- Siga su propio ritmo. No haga demasiadas actividades.
- Pida ayuda a otras personas. No intente hacer todo por sí solo.
- Tome breves descansos en sus actividades habituales. Piense en reducir la cantidad de horas de trabajo cuando los síntomas son intensos.
- Si piensa que la depresión o ansiedad está aumentándole el cansancio, consulte a su médico o profesional de la salud mental, o a ambos.
Cuídese la piel
- Consulte a su médico sobre el uso de cremas con corticosteroides para tratar los síntomas de la piel.
- Si le molesta la manera en que un salpullido causado por el lupus se le manifiesta en la cara o si tiene cicatrices causadas por el lupus, puede utilizar maquillaje, como Covermark, para cubrir el salpullido o las cicatrices.
- Manténgase fuera de los rayos del sol, sobre todo cuando son más fuertes, por lo general entre las 10 a.m. y las 4 p.m. Si va a exponerse al sol, cúbrase los brazos y las piernas, y use un sombrero. Asegúrese de usar un protector solar de amplio espectro que tenga factor de protección (SPF, por sus siglas en inglés) de 50 o más alto. Póngase más protector solar después de nadar, sudar o secarse.
Practique un buen cuidado personal
- Aprenda más sobre el lupus y cómo cuidarse.
- Tome los medicamentos exactamente según las indicaciones. Llame a su médico si tiene algún problema con los medicamentos.
- No fume. Si necesita ayuda para dejar de fumar, hable con su médico sobre programas y medicamentos para dejar de fumar. Estos pueden aumentar sus probabilidades de dejar el hábito para siempre.
- Siga una dieta equilibrada y saludable. Una dieta equilibrada incluye granos integrales, productos lácteos, frutas y verduras, y proteínas. Coma una variedad de alimentos de cada uno de esos grupos para obtener todos los nutrientes que necesita.
- Evite las infecciones como el COVID-19, los resfriados y la gripe. Hable con el médico sobre cualquier vacuna que pudiera necesitar, incluidas las vacunas contra el COVID-19, la gripe y el neumococo. Si de hecho se enferma o piensa que pudiera tener una infección, hable con el médico para que pueda tratar sus síntomas inmediatamente.
- Cepíllese los dientes y use hilo dental a diario. Visite al dentista dos veces al año.
- Hágase exámenes de la vista con regularidad.
- Establezca un sistema de apoyo con sus familiares, amigos y profesionales de la salud.
Sepa más
Mire
Créditos
Revisado: 25 septiembre, 2025
Autor: El personal de Ignite Healthwise, LLC
Comité de revisión clínica
Todo el material educativo de Ignite Healthwise, LLC es revisada por un equipo que incluye médicos, enfermeras, profesionales sanitarios avanzados, dietistas registrados y otros profesionales de atención médica.
Revisado: 25 septiembre, 2025
Autor: El personal de Ignite Healthwise, LLC
Comité de revisión clínica
Todo el material educativo de Ignite Healthwise, LLC es revisada por un equipo que incluye médicos, enfermeras, profesionales sanitarios avanzados, dietistas registrados y otros profesionales de atención médica.